Differentiating aragonite from calcite by IR and Raman spectroscopy
- Details
- Created: Monday, 30 March 2015 10:58
Aragonite and calcite are two polymorphs of the calcium carbonate mineral, CaCO3, calcite being the most stable. Aragonite's crystal lattice differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal system, respectively orthorhombic and trigonal. The CO32- ν4 in plane bend (antisymetric bending) vibrational internal mode gives for:
- aragonite: an IR reflection band / Raman peak doublet,
- calcite: a single IR reflection band / Raman peak .
Comparative spectra examples are given in Figure 1, 2 and 3 and the characteristic band / peak positions are summarized in Table 1 for all three spectroscopic methods.
Material |
Band / Peak |
IR | Raman | ||||
| IRS cm-1 (Figure 1) |
ATR cm-1 (Figure 2) |
Mode | cm-1 (Figure 3) |
Mode | |||
| Aragonite | doublet | weak | 700 | 700 | B2u | 715 | B2g |
| strong | 711 | 711 | B1u | 706 | B1g | ||
| Calcite | single | 711 | 711 | Eu | 715 | Eg | |
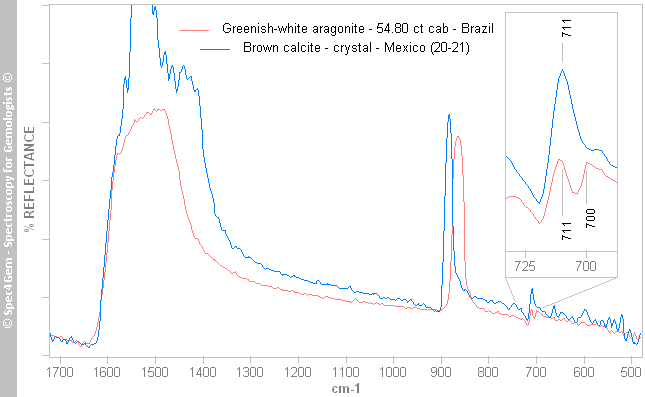 Figure 1. Infrared reflectance spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic reflection doublet at 700 and 711 cm-1 for aragonite although there is a single reflection band at 711 cm-1 for calcite.
Figure 1. Infrared reflectance spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic reflection doublet at 700 and 711 cm-1 for aragonite although there is a single reflection band at 711 cm-1 for calcite.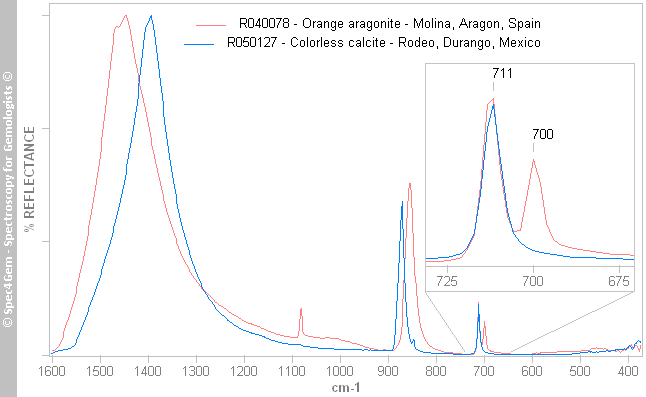 Figure 2. Infrared attenuated total reflectance spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic reflection doublet at 700 and 711 cm-1 for aragonite although there is single reflection band at 711 cm-1 for calcite.
Figure 2. Infrared attenuated total reflectance spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic reflection doublet at 700 and 711 cm-1 for aragonite although there is single reflection band at 711 cm-1 for calcite.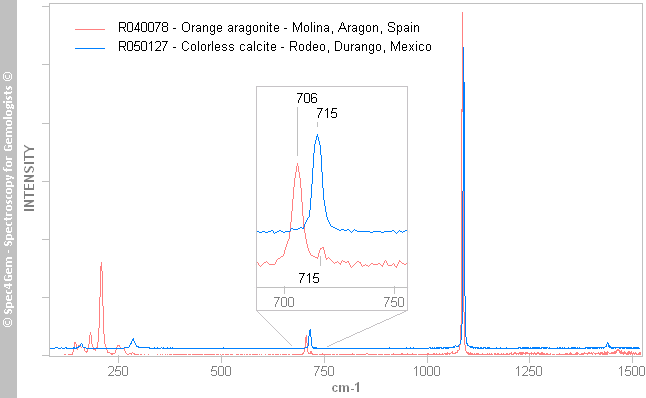 Figure 3. Raman spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic peak doublet at 706 and 715 cm-1 for aragonite although there is single peak at 715 cm-1 for calcite.
Figure 3. Raman spectra of aragonite (red) and calcite (blue), there is a characteristic peak doublet at 706 and 715 cm-1 for aragonite although there is single peak at 715 cm-1 for calcite.Note: Although IRS and ATR band positions are rather constant, the Raman peaks may slightly differ in literature.

